Why Drip Irrigation Could Be Best for You

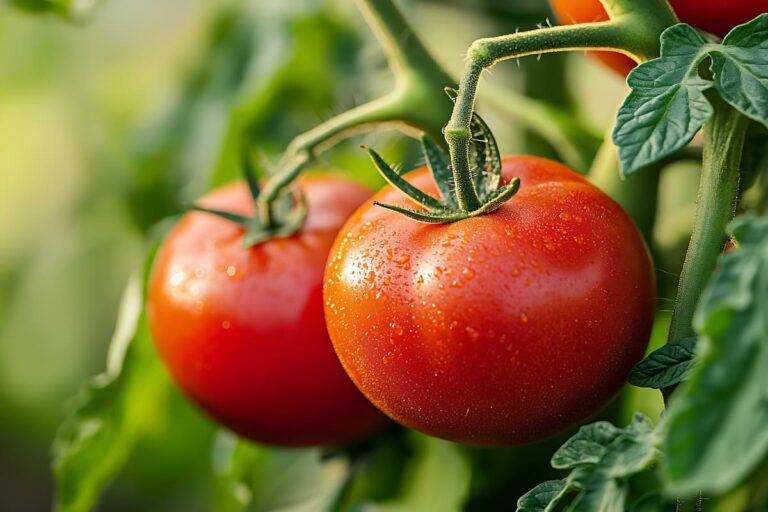
This article explains the benefits of a drip watering system and how it works. A drip irrigation system is any watering system that delivers a slow-moving supply of water at a gradual rate directly to the soil. Referred to as micro-irrigation or trickle irrigation, these systems consist of a network of pipes, tubing valves, and emitters.
For both small and large-scale watering operations, drip irrigation remains one of the most water and energy-efficient methods of irrigating.
Drip irrigation offers several great benefits. This includes conserving water, and energy, saving money on those bills, increasing plant health, and design flexibility. The tubing can be laid out to conform to any oddly-shaped landscape layouts. It can also extend to hanging planters, or extend down rows in a vegetable garden. Other applications include flowerbeds, ground cover, and street medians.
Drip Irrigation, Micro-Irrigation, and Sprinkler Systems
Although frequently used interchangeably, some would argue that drip irrigation and micro-irrigation are two distinctly different things.
Drip irrigation – a low-pressure, drip method of delivering water to the soil using either porous pipe or emitter tubes.
Micro-irrigation – all watering systems that use low-pressure sprays or misters.
How you refer to these forms of irrigation is not really relevant. It is important to be familiar with the options and benefits of both. That said, it is important not to confuse traditional sprinkler systems with micro-irrigation.
Traditional sprinkler systems, whether they use an impact, stationary, or rotary spray head, differ from micro-irrigation. These systems operate at much higher pressures. They deliver large quantities of water for a fixed amount of time. They work with long intervals between watering times.
Although micro-irrigation uses spray heads, they operate at considerably lower pressures. Micro-irrigation delivers much smaller quantities of water at frequent intervals.
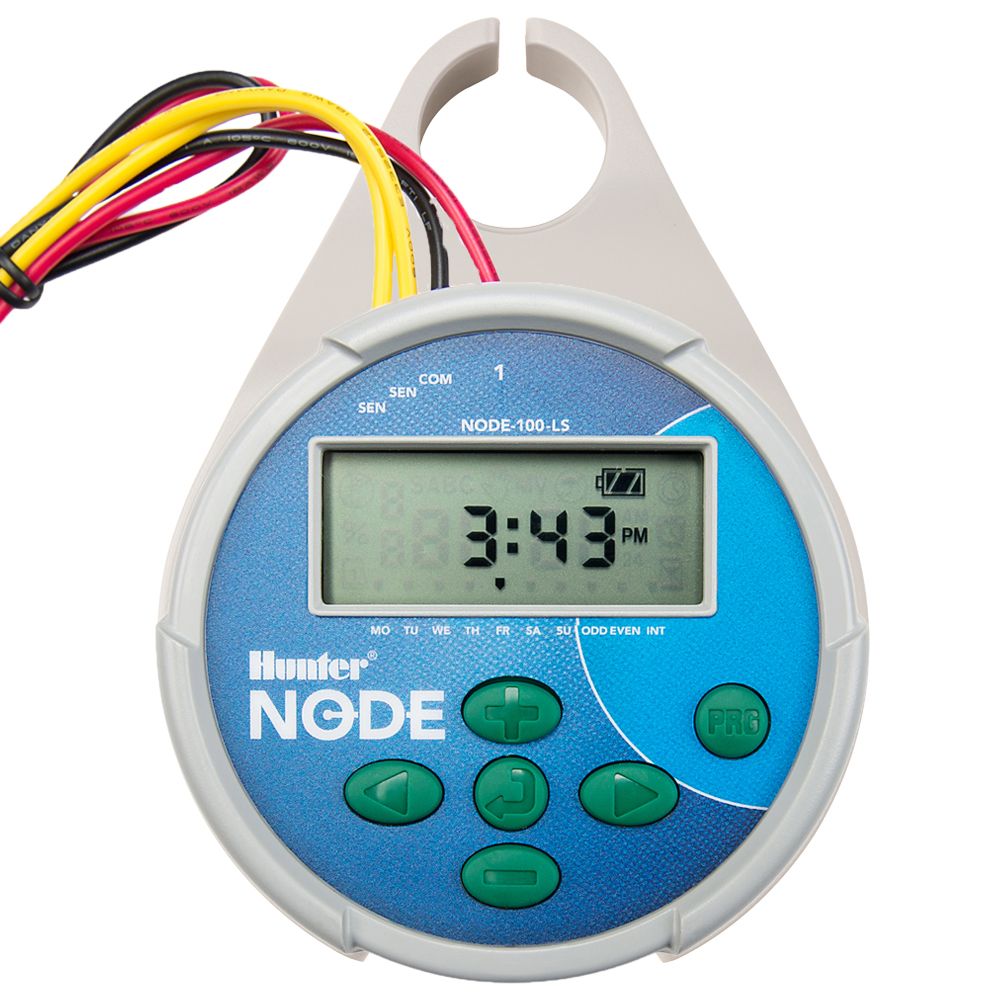
The image below shows the Hunter NODE 2 Station Battery Operated Controller. This controller includes an LCD display, start timer, and zone indication.

Drip Irrigation & Water Conservation
Typical sprinkler systems are, on average, about 75% water efficient, while drip irrigation systems have 90% or higher water efficiency. This is due to several key design differences.
- Water Pressure – High-pressure sprays deliver too much water too quickly. When it cannot be absorbed by the soil, it either puddles, which can be unhealthy for plants, or it runs off and is wasted. The slow delivery rate of drip irrigation allows the soil to absorb the water laterally, and maintain a uniform moisture level.
- Direct Watering – Water is applied directly to the soil surface and root zone, which minimizes evaporation and prevents water from running off or pooling. This leads to more efficient water use.
- Avoids Overwatering – Drip systems allow for precise control of the water amount delivered to each plant, avoiding overwatering. Sprinklers, on the other hand, can apply too much water at once, leading to overwatering.
- Reduced Wind Interference – Wind can easily blow water from sprinklers away from the intended plants, increasing water waste. Drip irrigation, being a ground-level system, is unaffected by wind, ensuring consistent water delivery regardless of weather conditions.
- No Watering of Unwanted Areas – Sprinkler systems often water non-plant areas such as paths, driveways, or between rows of crops, where water isn’t needed. Drip irrigation ensures water is delivered exactly where it is required, conserving water and ensuring better growth.
Drip Irrigation & Plant Health
A drip irrigation system helps with weed and disease control primarily by minimizing water contact with unwanted areas and reducing excess moisture on plant surfaces. Weeds thrive in moist environments, and traditional irrigation methods like sprinklers often wet large areas of soil, including spaces between plants. This provides ideal conditions for weed seeds to germinate and grow. In contrast, drip irrigation delivers water directly to the roots of your plants, keeping the soil between plants dry. With less water available in non-planted areas, weed growth is significantly reduced. Similarly, some plant diseases thrive in humid environments where leaves are frequently wet. A drip irrigation system applies water directly to the soil near the plant’s roots, keeping the foliage dry and reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
The increasing popularity of conservation, environmental friendliness, and the “green” movement have made drip irrigation a trendy choice, but it is a sound option for increasing plant health and saving money, as well. Drip systems are easy to design and install. They don’t require any trench digging and the above-ground tubing can be conformed to a variety of landscapes. This makes them a great option for avid do-it-yourselfers, and installing the system yourself will save a considerable amount of money.
Overall, drip irrigation is a great option, whether your goal is environmental and economic conservation, plant health, design simplicity, or all of the above.